Creative messages - the ability to generate new, unique and acceptable ideas that can be used as ways to solve communicative problems:
- What do we want to say and how?
- What kind of message do I need to create?
- Which transmission tools should be used?
- Who will deliver the message?
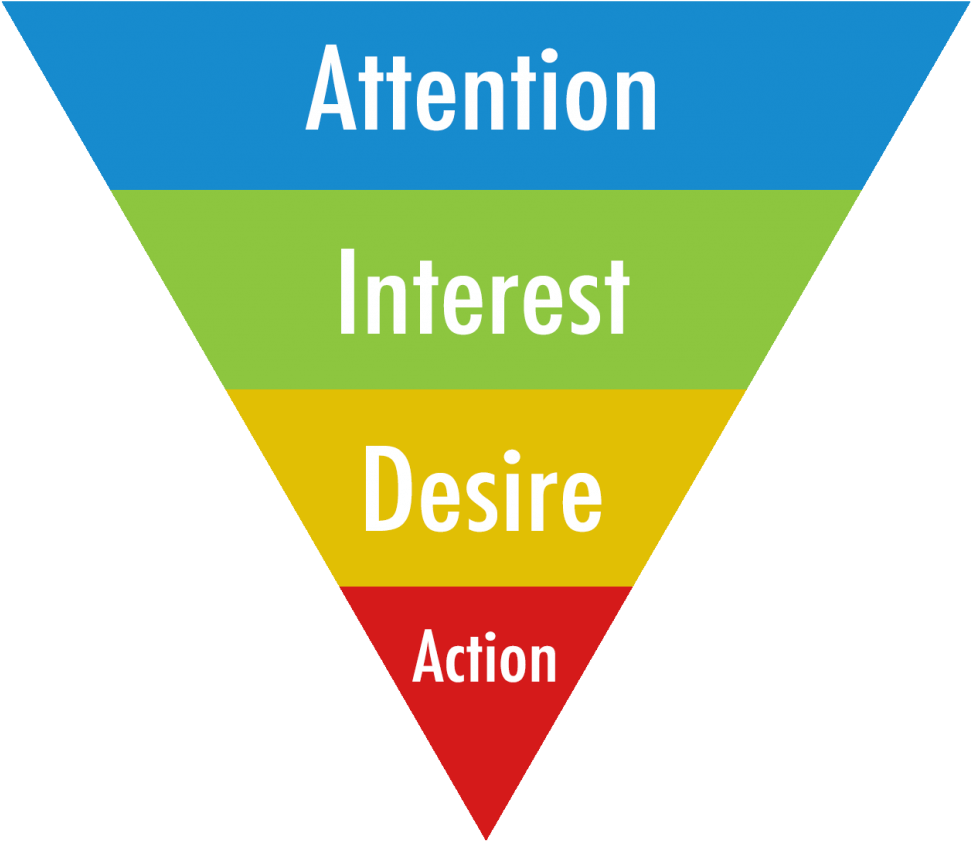
Communication messages are often formed by associating them with advertising by the gradualness of the effect on the user - the AIDA model:
- Attention - pay attention; Drawing attention is a necessary first step.
- Interest - generate interest; Once attention has been captured, it is necessary to generate interest in the product.
- Desire - to stimulate a desire to buy; Create a motive to buy the product.
- Action - trigger action; Encourage the consumer to buy.
What is creative advertising?
In order for advertising to deliver the right message, to the right person, at the right time, it must
būti:
- Relevance – ideas must mean something important to the audience.
- Original (Originality) - it must seem that such an idea has never occurred to anyone before.
- Impact (Impact) - advertising with impact has the power of "stopping" that comes from an intriguing idea, something the audience has never thought about.
This creativity determines The Big Idea , which expresses the original idea of advertising and forces a change in thinking.
What is important for creative messages to be understood?
The content of the creative message:
- A rational appeal - a tool that creates logical advertising information
delivered to consumers. - Emotional appeal - a tool that creates emotional advertising
information is communicated to users. - Moral appeal - a tool that creates valuable advertising information
delivered to consumers.
Rational crepe:
A rational crepe objectively and logically shows that the product can provide the desired benefits - it is more perfect, of better quality, more efficient, etc. Rational appeal is product-oriented and focuses on the practical, functional, utilitarian benefits that users want to obtain from the product. The main advertising appeal in the B2B sector.
Types of rational appeals (variations):
- Efficiency;
- Convenience;
- Cheapness;
- Naturalness;
- Intelligence;
- Productivity;
- Obedience;
- Independent;
- Health;
- Longevity;
- Modernity;
- Use of technology;
- Security;
- Neatness/cleanliness;
Emotional address
An emotional appeal tries to evoke positive or negative emotions that can motivate a purchase and is consumer-oriented and focuses on the social and/or psychological benefits consumers want to receive from the product. Mostly used in the B2C (business to customer) sector.
- Joy
- Love
- Sexuality
- Humour
- Nostalgic
- Proudly
- Security
- Fears
- Anger
- Sadness
- Guilt
- Shame
- Disgust
- Shocking
Moral appeal
Uses motifs directed at the audience's sense of morality, at the audience's perception of what is good and bad.
- Mostly used for social and
to solve ethical problems. - In certain situations, commercial organizations also use moral appeals to support socially responsible ideas.
There are several main types of moral (social) motives:
- The motive of justice. It is used in the advertisements of charity funds and public organizations.
- With the motive of environmental protection, it is called to save the environment.
- The motive of decency is related to basic moral principles (honesty, kindness, responsibility, etc.), for example, the call not to litter in the city, to pay off debts, etc. i.e.
- The motive of sympathy is aimed at the human ability to sympathize, to help another.
The structure of the creative message:
Each advertising message consists of:
- The main statement;
- Explanatory parts;
- Last argument;
Drawing conclusions:
- In a one-way message only positive arguments are presented. This is usually the message
more effective when the audience has formed a positive opinion about the communicated object,
less involved in the buying process, less educated. - In a two-way message both positive and negative arguments are presented. There are such messages
better when the audience is educated - they do not accept the final conclusions, they want to process it themselves
provided information and make decisions.
Creative message format:
The style of presentation of the advertising message, the real (physical) form of the message. The message format is influenced by the medium of transmission (channel, carrier).
Message types:
- Verbal;
- Visual;
- Both Verbal and Visual Verbal messages are more effective when the consumer is highly engaged in the buying process, while visual messages are more effective when the consumer is not involved in the buying process.





